Abstract
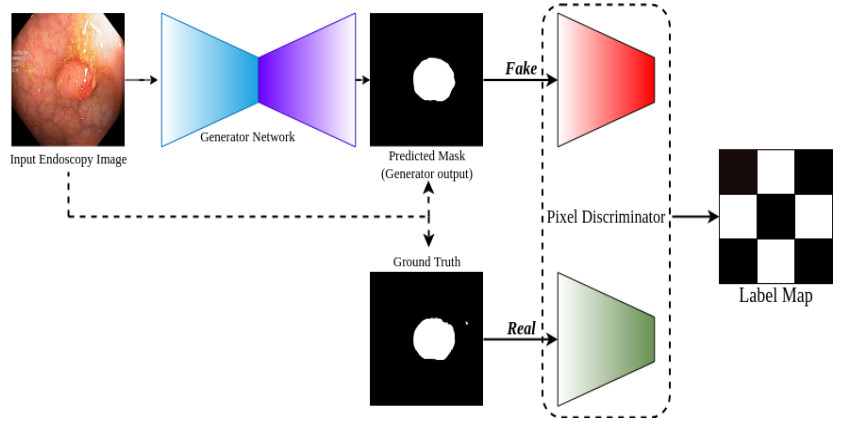
The Human Digestive System plays a crucial role in the nutrition supple- ment of the human body. Monitoring the digestive tract for deformations such as polyps can result in the prevention of fatalities like colo-rectal can- cer. Gastro-intestinal tract endoscopy is a prime diagnosis technique for the detection of such deformations. Diagnosis from images can be automated using the recent advancements in deep learning and AI. Apart from detec- tion, the exact segmentation of polyps can further aid the information to decide the extent of deformation and prescribe the course of treatment. It would also help the automated treatment systems for dissection of the polyp region. Image segmentation has been addressed using different techniques including CNNs and loss functions. But less emphasis was made on utiliz- ing Generative Adversarial Networks in Medical Image segmentation tasks. In our approach, we formulated Polyp Segmentation as an Image-to-image translation task using conditional GANs. We conducted a rigorous experi- mental study to prove that our approach delivers better efficiency in terms of qualitative and quantitative results. We experimented with different combi- nations of Generator architectures, GAN training schemes, and loss functions and showed the comparative study. We used standard datasets for training our experimental setup and proving the generality of our approach.
This work is completed as Part-1 of my Master’s Thesis at IIT Gandhinagar under the supervision of Dr. Shanmuganathan Raman.